世界的にPFAS(永久化学物質)の使用禁止が徐々に実施される中、PFASフリーのフライパンや健康的な素材で作られたその他の調理器具の需要がかつてない伸びを見せている。多くの欧米諸国における規制が市場の変化を加速させている。例えば、欧州連合(EU)は2025-2026年までにPFASを含む台所用品を完全に禁止する予定であり、米国のいくつかの州はすでに事前に規制を実施している。これは、政策レベルが食品の安全性を重視していることを反映しているだけでなく、パンデミック後に消費者が健康的な食生活や持続可能なライフスタイルに関心を寄せているという社会的傾向とも一致している。市場データによると、欧州と北米におけるPFASフリーのフライパンやその他の調理器具の売上は、2024年には前年比20%以上増加し、中でもセラミックコートとステンレスの多層調理器具が特に人気であった。メーカーにとって、これは挑戦であると同時にチャンスでもある。安全で耐久性に優れ、高性能のフッ素フリー調理器具を最初に提供できる企業は、世界的な台所用品競争の新ラウンドで優位に立つだろう。
PFASとは何か、なぜ禁止されているのか
PFAS(Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances)は合成有機フッ素化合物の一種で、PFOAやPFOSなど数千種類の化学物質を含む。高温、水、油に強く、腐食しにくく、化学的性質が非常に安定している。ノンスティックフライパンのコーティングに広く使用されている。PFASは自然環境ではほとんど分解せず、人体や動物、植物に長期間蓄積する「永遠の化学物質」として知られている。科学的研究によれば、PFASへの長期的な暴露は、がんの発生率を高め、肝機能を損傷し、免疫系を抑制し、胎児の発育に影響を及ぼす可能性がある。PFASの広範な使用と持続的な汚染のため、世界中の多くの国が、環境危害の低減と公衆衛生の保護を目的として、PFASを制限または禁止すべき物質としてリストアップしている。
欧米市場におけるフライパンの現状とニーズ
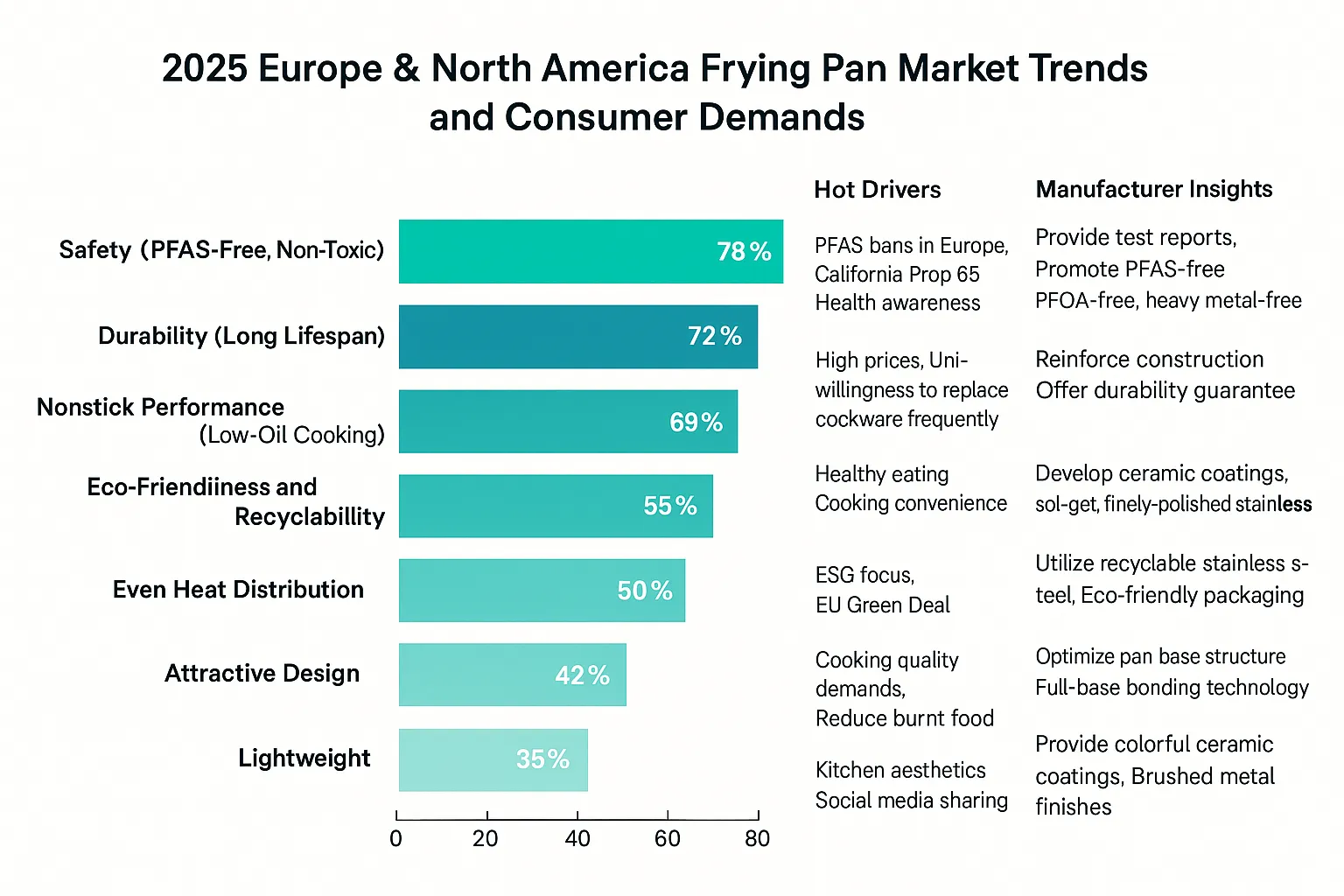
現在、欧米市場におけるPFASフリーフライパンの需要は、健康、安全性、耐久性、持続可能性という4つの大きな方向性を核とした包括的なアップグレードが行われており、細部においてもより高い基準が設けられている。
健康と安全
規制主導:EUのREACH規則は、10,000以上のPFAS化学物質に規制を課している。米国環境保護庁(EPA)は段階的禁止計画を開始し、カリフォルニア州提案65号も有害物質の厳格な表示を義務付けている。
素材の条件:100% PFASフリーのフライパンで、PFOA、PTFE、鉛、カドミウム、ニッケルなどの潜在的に危険な成分を含まないこと。
認証基準:欧米の消費者は、LFGB(ドイツ食品接触安全認証)、FDA、ISO9001、SGS食品安全テストなど、複数の認証に合格した製品を信頼している。
耐久性基準
耐熱性:260℃から300℃の高温での長時間の調理に耐え、変形や剥離がないこと。
耐スクラッチ性テスト:輸入業者によっては、メタルスクレーパーによる5,000回以上の耐スクラッチ性テスト、または30分間のドライバーニングでコーティングが損傷しないことを条件とするところもある。
熱伝導の均一性:鍋底の厚さは2.0mm以上とし、3層構造の複合底または同等の熱伝導構造とする。食材の局部的な過熱や焦げ付きを防ぐため、熱差は±5℃以内に制御する。
ノンスティック性能(PFASフリー代替品)
主流のソリューション:高級市場ではセラミック・コーティングやゾル・ゲ ル・コーティングが好まれる。一部のシェフやレストランでは、鏡面仕上げのステンレスの素鍋に油脂を塗って使用する傾向がある。
耐久期間:輸入業者は、家庭用として少なくとも2年間(約5,000回の調理サイクル)こびりつきにくさを維持できるPFASフリーのフライパン製品を選ぶ傾向がある。
洗浄が簡単:ほとんどの残留物はきれいな水で洗い流すことで除去できることが求められ、化学洗浄剤の使用を減らすことができる。
持続可能性と環境保護
マテリアルリサイクル:リサイクル可能なステンレススチール(304/316など)、リサイクルアルミニウムを使用し、プラスチック部品を削減する傾向にある。
生産環境保護:ブランドによっては、生産工程におけるエネルギー使用量、廃水処理量、排出量が基準を満たしていることを証明するために、カーボンフットプリント報告書の提出を求めるところもある。
包装のトレンド:発泡プラスチックを、プラスチックフリーの分解可能な紙包装や再利用可能な布袋に置き換える。
デザインと機能の詳細
コンロの互換性:IHコンロ、ガスコンロ、電気コンロ、セラミックコンロなど、すべてのプラットフォームに対応していること。
人間工学:ハンドルは、耐熱性、滑り止め、200℃以上のオーブン温度に耐えられ、握りやすいものでなければならない。
鍋蓋の機能欧米市場ではビジュアル重視のガラス製鍋蓋が好まれ、オーバーフロー防止設計と密閉性能が要求される。
代替コーティング:セラミック、ゾル-ゲル、ステンレス鋼ベアポット
セラミック・コーティング
はじめにシリカを主成分とし、高温硬化により皮膜を形成し、PFASやPFOAを含まない。
利点耐熱性(450℃まで)、健康と安全性、多様なカラーバリエーション、自然なノンスティック効果。
欠点:コーティングは硬いがもろい。頻繁に落としたり、金属製のシャベルで使用すると寿命が短くなる(家庭用で約1~2年)。
対象者健康や身だしなみに気を配るファミリーユーザー。
ゾル・ゲルコーティング
はじめにゾル-ゲル法によって形成された無機/有機混合皮膜は、従来のセラミックスよりも高い硬度と接着性を有する。
利点PFASを含まず、耐スクラッチ性に優れ、300℃以上の耐熱性があり、脱落しにくい。
欠点:非粘着性はセラミックよりやや劣り、最良の効果を得るにはグリースと併用する必要がある。
該当するグループレストラン、よく利用する家庭、耐久性を追求する人。
ステンレス多層複合底ベアポット(SS 304/SS 316)
はじめにステンレス鋼 + アルミニウム(または銅)複合構造、非コーティングデザイン、表面研磨またはブラッシング、食品自体に固執しないように油に依存しています。
利点耐用年数が長い(5年以上)、コーティングが全くない、超高温(500℃以上)に耐えられる、均一に加熱できる、局所的な過熱による鍋へのこびりつきが少ない。
デメリット製造コストが高い、調理技術(油の温度管理)が必要、初心者はフライパンにこびりつきやすい。
該当するグループ均一な調理を追求する人、料理愛好家、長寿命と高温調理を求める人。
PFASフリーのフライパンを安全な素材でより丈夫に、こびりつきにくくする方法
PFASコーティングを施さずに(つまり、PTFEやPFOAなどのフッ素コーティングを使わずに)、中華鍋の耐久性とべたつきのなさを両立させるためには、材料の選択、表面処理、構造の最適化の3つの側面から努力することができる。
素材の選択(耐久性のある基礎)
ステンレス304/316:耐腐食性、長寿命、食品に接触しても安全性が高い。
表面処理工程(非粘着性の鍵)
鏡面研磨:ステンレスの内面を鏡面に近い状態に研磨することで、食品と金属の接触部分を減らし、卵などが滑りやすくする。
マイクロテクスチャー:鍋の表面に極めて微細なテクスチャーを作り、食品との接触面積を減らすと同時に、油膜層を保護する。
プラズマ・セラミック・コーティング:安全性と耐摩耗性の両方を考慮し、金属表面に超硬質セラミック層を形成できる新技術。
構造の最適化
三層コンポジット+ゾルゲル+セラミック表面層(推奨組み合わせ)
利点均一な熱伝導、良好な塗膜密着性、耐スクラッチ性、ハイエンド/中高級市場に適している。
デメリット高コストと複雑なプロセス(硬化曲線を最適化する必要がある)。
純ステンレス鋼304+レーザー微細構造+ゾル-ゲル/セラミック
メリット食品安全性、耐腐食性、高級感、レーザー加工による焦げ付きにくさ。
欠点:裸のステンレス鋼は熱伝導が遅いため、熱伝導を良くするために厚くするか、底を複合材にする必要がある。
お問い合わせ
私たちはプロフェッショナルです。 PFASフリーフライパンメーカー 20年以上の生産経験を持つ。欧米市場の厳しい品質基準をクリアした製品を、幅広い仕様とデザインスタイルで長年提供しています。また、ハンドル、コーティング、蓋、ロゴやパッケージに至るまで、あらゆるカスタマイズにも対応しています。高度な生産設備と厳格な品質管理システムにより、すべてのPFASフリーフライパンが安全性、耐久性、熱伝導性能、外観の細部において国際基準を満たしていることを保証いたします。大量購入でも ブランドOEM/ODM, また、小売や電子商取引のための差別化された製品を作成するために、我々は効率的なワンストップソリューションを提供することができます。お問い合わせ、お見積もり、サンプルのご請求をお待ちしております。








